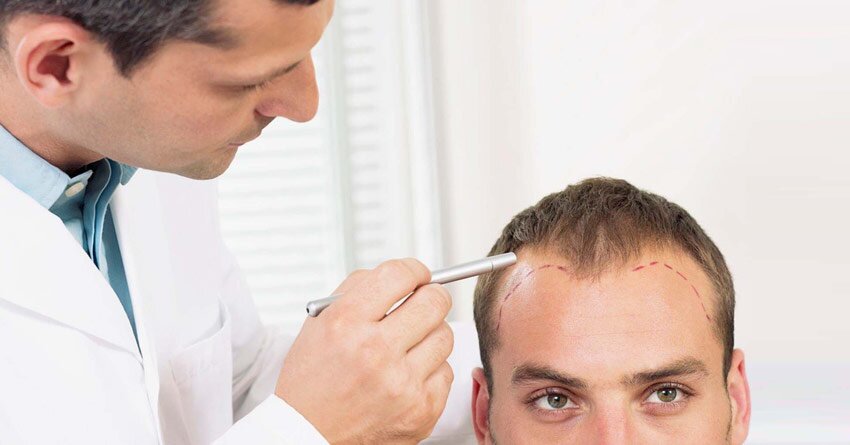
What is hair transplantation ?
Hair transplant is a surgical procedure to replace bald patches on the head or any other part of the body . Generally hair Transpalnt is a cosmetic procedure done to increase or improve beautification of the patient . Hair transplantation can be done on both males and females .Hair Transplant is done be transplanting hair follicles containing hair from donor site of the patient itself to the recipient site . In hair transplantation procedure the grafts used are Autografts . The grafts can be obtained from the donor site of head or it can also be taken from other areas chest , underarms , public hair etc of the patient .Hair transplantation can be done on head , forehead , eyebrows , eyelashes , scared tissues etc
Types: Generally two types of hair Transplantation techniques we use are :
1 FUE: Follicular unit extraction ( single follicles are extracted and implanted in the recipient site ( this modern , and semi surgical method . FUE ( Follicular Unit Extraction) is done using a tiny 0.7mm-1mm diameter punch attached to a micro-motor. The physician will then one by one remove individual follicular units from the patient’s scalp. The micro-motor punch makes a tiny circular incision around the follicular unit to separate the follicular graft. The grafts are then taken out individually from the scalp using a jewellers forceps, and then collected by hair technicians in sterile petri-dishes. The extract follicles are then immediately be placed to a bladed area on the scalp, to create a density close to the natural one.
2. FUT : Follicular unit transplantation ( in this technique , part of the skin from back of the head is removed by surgery and then the follicles are separated and implanted in the recipient site . The donor area is then pulled together and sutured.
FUT (Follicular unit Transplantation): Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT) also know as Strip Technique in which a long portion of the skin behind the head (donor area) is removed and then individual follicles are removed from that strip via stereo-microscopic dissection. The wound edges are then closed by suturing which leaves a single, generally fine scar.